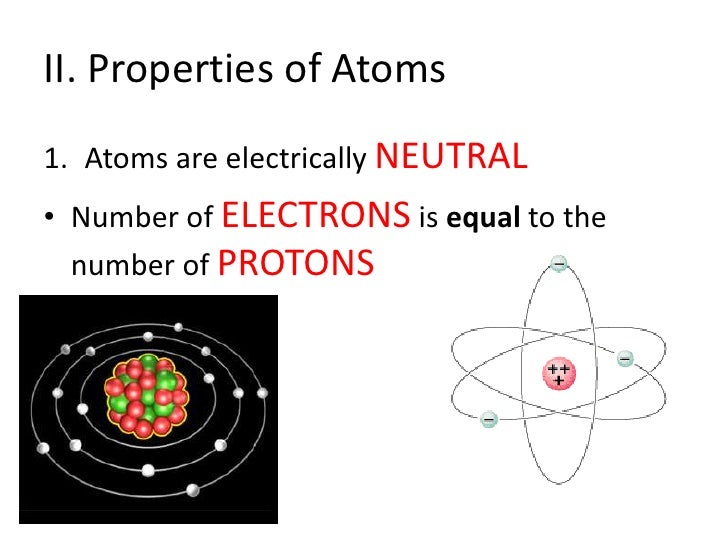
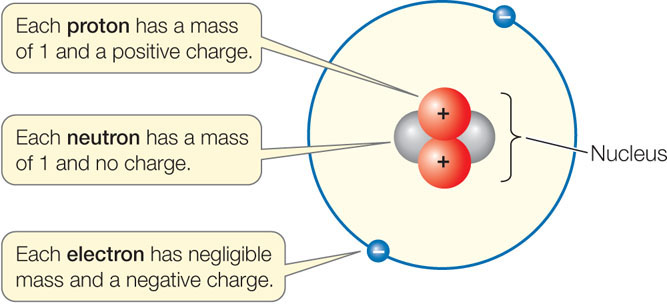
Atoms of matter are electrically neutral because their nuclei contain the same number of protons as there are electrons surrounding the nuclei. Electric current and charged objects involve the separation of some of the negative charge of neutral atoms. Key Takeaways: Number of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive electrical change, while electrons are negatively charged, and neutrons are neutral. A neutral atom has the same number of protons and electrons (charges cancel each other out). Interstellar neutral atoms are unsuitable for heliopause mapping because they penetrate deep into the heliosphere. Most of the glow of heliospheric neutrals, as seen by an observer near 1 AU, would originate within the 10-AU region.
Category: Chemistry Published: June 7, 2013
Atoms do not always contain the same number of electrons and protons, although this state is common. When an atom has an equal number of electrons and protons, it has an equal number of negative electric charges (the electrons) and positive electric charges (the protons). The total electric charge of the atom is therefore zero and the atom is said to be neutral. In contrast, when an atom loses or gains an electron (or the rarer case of losing or gaining a proton, which requires a nuclear reaction), the total charges add up to something other than zero. The atom is then said to be electrically charged, or 'ionized'. There is a major difference between the neutral state and the ionized state. In the neutral state, an atom has little electromagnetic attraction to other atoms. Note that the electric field of a neutral atom is weak, but is not exactly zero because the atom is not a point particle. If another atom gets close enough to the atom, they may begin to share electrons. Chemically, we say that the atoms have formed bonds.

Atoms Of Magnesium Are Neutral Because They Contain The Same Number Of Electrons And
- Atoms as a whole are neutral because a. The numbers of neutrons exceeds that of protons or electrons.
- All atoms have the same number of electrons as protons, so the positive and negative charges 'cancel out', making atoms electrically neutral. 4.5: Elements- Defined by Their Numbers of Protons Scientists distinguish between different elements by counting the number of protons in the nucleus.
In contrast to neutral atoms, the field due to an ionized atom is strong, even at larger distances. The strong electric field of ions makes them strongly attracted to other atoms and molecules, to the point of being highly chemically reactive. Ionized atoms can be free radicals, which are atoms with a dangling bond that are highly reactive. In the human body, free radicals can react with DNA, leading to mutations and possibly cancer. Atoms become ionized when light with enough energy knocks off some of their electrons. Only light waves at the frequencies of X-rays and gamma rays have enough energy to ionize atoms and therefore lead to cancer. The cancer-causing power of only certain frequencies is why you can use your cell phone as much as you want, but you can only get an X-ray image taken on rare occasions. Free radicals occur naturally in your body. They only become dangerous when there are more free radicals than your body can handle.
But not all ions in the body are bad. Because of the charged nature of ions, the human body makes use of them to pass electric signals through nerves. The body also uses ions to control fluid levels and blood pressure. The most-used ions in the human body are sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium and chloride. Ions are also created whenever you electrostatically charge an object, such as when you rub a balloon on your hair. For this reason, your clothes dryer machine can be thought of as an ion maker. As clothes rub together in the machine, electrons get knocked from one atom to another. The result is the all-too familiar static cling. Electricity and strong electric fields do a good job of creating ions (think lightning).
The neutral state of an atom is typically the most stable configuration (unless molecular bonds and the chemical environment complicates the picture), so ions tend to discharge and return to their neutral state over time. The reason for this is that, as an ion, the atom has a strong electric field that attracts the needed electron or the needed atom to take its extra electron. But once the atom becomes neutral, it has an equal number of electrons and protons, it does not have a very strong field, and therefore has little possibility of changing.
Because Atoms Are Electrically Neutral The Number Of Protons And
Atoms vs. Ions
Atoms are neutral; they contain the same number of protons as electrons. By definition,an ion is an electrically charged particle produced by either removing electronsfrom a neutral atom to give a positive ion or adding electrons to a neutralatom to give a negative ion. When an ion is formed, the number of protonsdoes not change.
Neutral atoms can be turned into positively charged ions by removing oneor more electrons. A neutral sodium atom, for example, contains 11 protonsand 11 electrons. By removing an electron from this atom we get a positivelycharged Na+ ion that has a net charge of +1.

Atoms Are Neutral Because They Have The Same Number Of
Atoms that gain extra electrons become negatively charged. A neutral chlorineatom, for example, contains 17 protons and 17 electrons. By adding one moreelectron we get a negatively charged Cl- ion with a net charge of -1.
The gain or loss of electrons by an atom to form negative or positive ionshas an enormous impact on the chemical and physical properties of the atom.Sodium metal, for example, which consists of neutral sodium atoms, burstsinto flame when it comes in contact with water. Neutral chlorine atoms instantlycombine to form Cl2 molecules, which are so reactive that entire communities are evacuatedwhen trains carrying chlorine gas derail. Positively charged Na+ and negatively charged Cl- ions are so unreactive that we can safely take them into our bodies wheneverwe salt our food.